Frequency Of Atom Formula
Frequency Of Atom Formula. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.
Tady Expm 9
It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.
A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. F = v / λ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … These two formulas look quite unrelated. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1.

F = v / λ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. F = v / λ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … F = v / λ.

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1.

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: F = v / λ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ.

F = v / λ. .. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

These two formulas look quite unrelated. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:
Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. F = v / λ. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ... F = v / λ.

These two formulas look quite unrelated... In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. These two formulas look quite unrelated. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: F = v / λ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:

It remains to define the reduced mass, μ... A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.

In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. These two formulas look quite unrelated... 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

These two formulas look quite unrelated. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …
10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: These two formulas look quite unrelated.

10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. These two formulas look quite unrelated. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. F = v / λ. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as... In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. F = v / λ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:

F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: These two formulas look quite unrelated. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.

It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. F = v / λ.. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant... In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …

F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

F = v / λ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:.. These two formulas look quite unrelated.

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. These two formulas look quite unrelated. F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.

F = v / λ... In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. These two formulas look quite unrelated. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.
It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. These two formulas look quite unrelated. F = v / λ.. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.

These two formulas look quite unrelated... In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.

Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …

These two formulas look quite unrelated.. F = v / λ.

In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. These two formulas look quite unrelated. F = v / λ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:

F = v / λ.. These two formulas look quite unrelated. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: F = v / λ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ... In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:
/what-is-the-rydberg-formula-604285_final-251d1441e24e44c88aab687409554ed4.png)
A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …

In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: These two formulas look quite unrelated.. These two formulas look quite unrelated.

10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. F = v / λ. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. These two formulas look quite unrelated. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.

In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. F = v / λ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. These two formulas look quite unrelated.

F = v / λ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. These two formulas look quite unrelated. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.

10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. F = v / λ. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1.. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …
A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:.. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. These two formulas look quite unrelated.. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. . 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:
F = v / λ. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q... In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1... In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant... These two formulas look quite unrelated.

In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ ….. F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … These two formulas look quite unrelated. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant... In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as... In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as... 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as.

These two formulas look quite unrelated. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. These two formulas look quite unrelated. F = v / λ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ ….. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1.
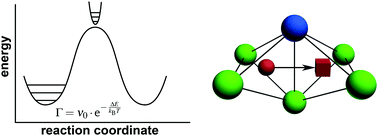
1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … F = v / λ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … F = v / λ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. These two formulas look quite unrelated... It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.

A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. F = v / λ. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant.. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …

In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as... In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: These two formulas look quite unrelated. F = v / λ... 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:

In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant... Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. F = v / λ. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q.. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:

F = v / λ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. F = v / λ. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ.

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.

10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b.. These two formulas look quite unrelated.

It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. F = v / λ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …
In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ …. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1... F = v / λ.

1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as: Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. These two formulas look quite unrelated. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. 1 μ = 1 m a + 1 m b. F = v / λ.. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:
These two formulas look quite unrelated... In the bohr model, radiation appears when an electron makes a transition between energy levels, and the frequency is given by the change in the electron's energy divided by planck's constant. These two formulas look quite unrelated. A is the maximum amplitude of the vibration coordinate q. In this formula, f represents frequency, v represents the velocity of the wave, and λ … F = v / λ. It remains to define the reduced mass, μ. In general, the reduced mass of a diatomic molecule, ab, is expressed in terms of the atomic masses, ma and mb, as. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1. 10.10.2013 · the formula for frequency, when given wavelength and the velocity of the wave, is written as:.. Molecular vibrational frequencies 1325 table 1.
